State of the Basin
The Nile River Basin State of the Basin Report (SOB) (NBI, 2020) describes the complex multi-faceted challenges facing the Nile basin and its inhabitants and highlighted some major challenges:
Increasing pressure on water resources. The Nile waters are coming under increasing pressure for various productive and environmental purposes, and demand driven by population growth and socio-economic development continues to rise.
Increasing pressure on water resources. Implications of agricultural development for water and food security. Irrigated agriculture is by far the biggest consumer of the Nile waters and the trend is an increasing one. Current yields and irrigation efficiencies are generally poor.
Access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy is increasing, but electricity supply in most Nile countries, is inadequate. Hydropower and renewables can play a major role in the future.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity which include the rich natural resources and outstanding biodiversity in the Nile Basin face unprecedented threats.
Improving resilience to climate change impacts is a challenge that cuts across the already mentioned challenges.
Transboundary water Governance.Active and constructive political commitment to transboundary cooperation continues but there is a need to formalise this cooperation through the enactment of the Nile Cooperative Framework Agreement.
Socio-economic Outlook
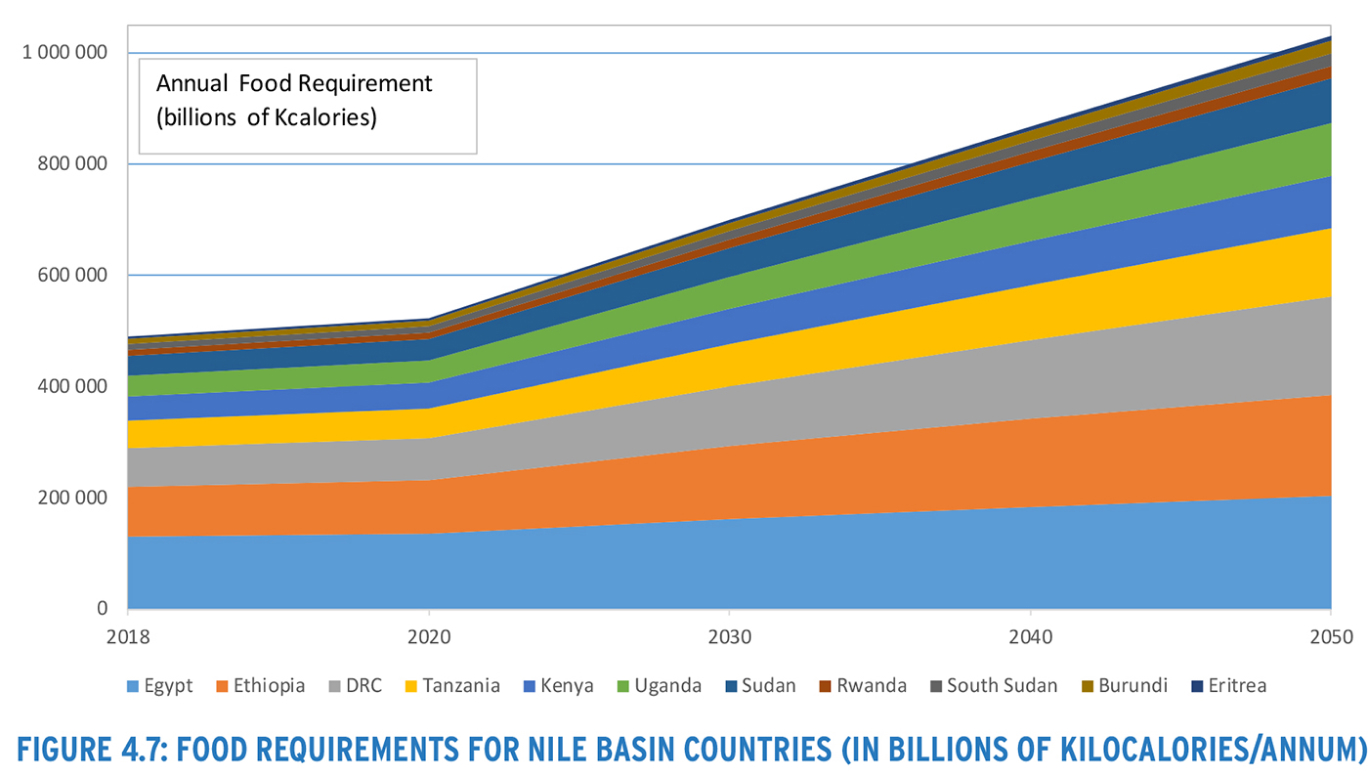
The evolution of socio-economic conditions in the basin countries will have an important influence on food and energy demand, and on water demand for domestic purposes. This evolution reflects changes in population, urbanization, and overall economic development and their connection to living standards. These aspects are investigated in Chapter 4 of the NRBMP in order to provide context for what needs to be done by way of preparation.