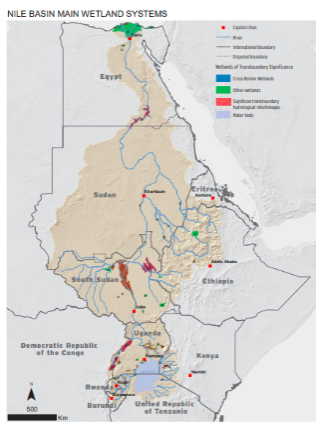
The Nile and its main tributaries flow through several large wetlands of great relevance for biodiversity conservation. These wetlands provide important regional and local ecosystem services: They supply water, protect people from floods, reduce droughts, control erosion, improve water quality and hydrology, critical habitat for biodiversity, store carbon, support livelihoods and provide other functions critical to achieving sustainable development within the Nile Basin. Yet, these valuable eco-systems are threatened by pollution, siltation, conversions into agricultural land, settlement, infrastructural development, climate change and deforestation.
NBI works with member countries to build a better understanding of the services and value provided by wetlands of transboundary significance and developing concrete interventions to manage and maintain these ecosystems (see also our work on Environmental Flows).
What is a Wetland?
A wetland is an area covered or submerged by surface or groundwater supporting plants and animals, typically adapted for life in water-saturated soil conditions. The term “wetland” is applied to a broad range of different habitats and ecosystems including swamps, flood plains, seasonally flooded grasslands, the edges and shallow waters of rivers and lakes, estuaries and coastal marshes, as well as mangroves and peat bogs. It also includes man-made or constructed wetlands.
The NBI Wetlands Management Strategy was approved by the Nile Council of Ministers (Nile-COM) in 2013 and provides the strategic implementation framework for the transboundary management of Nile Basin wetlands to guide their sustainable utilization.
NBI maps and provides key data on transboundary wetlands, including their extent, their hydrological characteristics, provided ecosystem services and the biodiversity situation. NBI has also carried out a model-based assessment of the regulatory function (low flow au...
Building a knowledge base on Nile Basin Wetlands
NBI maps and provides key data on transboundary wetlands, including their extent, their hydrological characteristics, provided ecosystem services and the biodiversity situation.
NBI has also carried out a model-based assessment of the regulatory function (low flow augmentation, groundwater recharge, flood buffer) and water budget of each major wetland in the Nile system.
Related Resources:
The wetlands of the Nile Basin provide a wide range of critical ecosystem services: They supply water, protect people from floods, reduce droughts, control erosion, improve water quality, provide critical habitat for biodiversity, store carbon, support livelihoods an...
Ecosystem Services
The wetlands of the Nile Basin provide a wide range of critical ecosystem services: They supply water, protect people from floods, reduce droughts, control erosion, improve water quality, provide critical habitat for biodiversity, store carbon, support livelihoods and more.
In order to ensure that wetlands are able to continue to provide the wide range of ecosystem services, countries must sustain certain minimum water flows, or environmental flows.
Environmental Flows
In order to ensure that wetlands are able to continue to provide the wide range of ecosystem services, countries must sustain certain minimum water flows, or environmental flows.
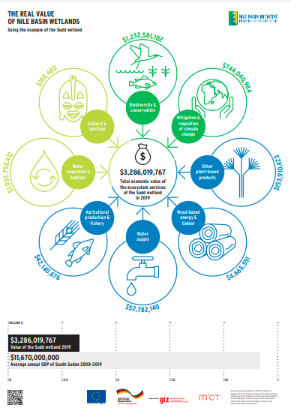
Wetlands provide services of huge economic importance to the Nile Basin. Individual case studies to estimate this economic value were carried out for the wetlands of the Sio-Siteko between Kenya and Uganda, the Semliki Delta between Uganda and the Democratic Republic...
The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)
Wetlands provide services of huge economic importance to the Nile Basin. Individual case studies to estimate this economic value were carried out for the wetlands of the Sio-Siteko between Kenya and Uganda, the Semliki Delta between Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Mashar Marshes and Sudd in South Sudan, the Lower Baro Wetland between Ethiopia and South Sudan, and the Rweru-Bugesera Transboundary Wetlands Complex between Rwanda and Burundi.
The Nile Basin’s wetlands and peatlands store vast amounts of carbon. NBI has calculated the current carbon stock in the basin and estimated the CO2 emissions from drained use; developing a discussion paper which can serve as the backbone for further discussions on e...
Wetlands and Climate Change
The Nile Basin’s wetlands and peatlands store vast amounts of carbon. NBI has calculated the current carbon stock in the basin and estimated the CO2 emissions from drained use; developing a discussion paper which can serve as the backbone for further discussions on emissions avoidance from wetlands and peatlands in the region.
DR Congo, Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda, with the coordination of NELSAP, have developed and approved three Conservation Investment Plans (CIPs) for the transboundary wetland landscapes on Sio-Siteko (Kenya/Uganda), Sango Bay/Minziro (Tanzania/Uganda), and Semliki Delta...
Transboundary Wetlands Management and Investment Plans
DR Congo, Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda, with the coordination of NELSAP, have developed and approved three Conservation Investment Plans (CIPs) for the transboundary wetland landscapes on Sio-Siteko (Kenya/Uganda), Sango Bay/Minziro (Tanzania/Uganda), and Semliki Delta (DR Congo/Uganda). The CIPs were prepared to support conservation measures of these biologically rich landscapes through delivery of the implementation framework emanating from three preceding Transboundary Wetland Management Plans (2020-30) - again, for Sio-Siteko, Sango Bay/Minziro, and Semliki Delta respectively. The financing needs outlined in the CIPs are designed to harmonise, integrate and align with existing interventions in the wetland landscapes, and are targeted at development partners, private and public investors as well as government agencies with an interest in conserving transboundary wetland landscapes and the ecosystem services in the region.
The Sudd Wetland, one of the world’s largest, is located in South Sudan and recognized under the Ramsar Convention as a Wetland of international importance. In close coordination with South Sudan, NBI has developed a Baseline and Action Plan, Description of the hydro...
The Sudd
The Sudd Wetland, one of the world’s largest, is located in South Sudan and recognized under the Ramsar Convention as a Wetland of international importance. In close coordination with South Sudan, NBI has developed a Baseline and Action Plan, Description of the hydrologycal model, TEEB study and Environmental Flow Assessment, to improve the state of knowledge and recommend actions for the sustainable and effective management of the Sudd.
NBI supports countries in assessing certain aspects of significant cross-border wetlands where the demand or relevance is particularly high. The work on the wetlands of the Mara has laid the foundation for a cross-border Water Allocation Plan between Kenya and Tanzan...
Other significant cross-border wetlands
NBI supports countries in assessing certain aspects of significant cross-border wetlands where the demand or relevance is particularly high. The work on the wetlands of the Mara has laid the foundation for a cross-border Water Allocation Plan between Kenya and Tanzania, while an assessment of the Mashar Marshes between Ethiopia and South Sudan has enhanced the knowledge base for a hitherto little studied wetland landscape.
Wetlands Governance is key for enabling adequate management and sustainable use of ecosystem services at the landscape level. NBI has developed several national wetland governance reports which cover dimensions such as institutional arrangements for wetland managemen...
Wetlands Governance
Wetlands Governance is key for enabling adequate management and sustainable use of ecosystem services at the landscape level. NBI has developed several national wetland governance reports which cover dimensions such as institutional arrangements for wetland management (Ministry, Agency), policies (and laws) in place, Ramsar membership and sites, national programs, listing of specific wetland related measures in national biodiversity (Aichi), Ramsar and climate (NDC) action plans, etc.
The Nile Basin Wetlands Forum is a multi-stakeholder dialogue platform established by the Nile Basin Initiative (NBI) in 2016 for the purpose of mobilizing and coordinating state and non-state actors to take appropriate action to protect and conserve wetlands of tran...
Wetlands Forum
The Nile Basin Wetlands Forum is a multi-stakeholder dialogue platform established by the Nile Basin Initiative (NBI) in 2016 for the purpose of mobilizing and coordinating state and non-state actors to take appropriate action to protect and conserve wetlands of transboundary significance in the Nile River Basin.